| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
Midpoint between two points:

|
|
| |
| | |
Distance between two points:

|
|
 |
|
Function Notation:
y = mx + b
f(x) = mx + b
f = {(x,y)| y = mx + b}
|
|
 |
Slope-intercept form of the equation of a line.
y = mx + b where
m is the slope, and
b is the second coordinate of the y-intercept
|
|
| |
Inverse Notation:
for the function f,
the inverse of f is denoted as f -1
f -1( f(x) ) = x and
f( f -1( x ) ) = x
|
|
|
Definitions of slope:
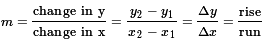
|
|
| |
| | |
| Given an equation, graph the line |
|
| |
| | |
| Given the graph of a line, write the equation |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
| Standard Form
Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers,
(A is non-negative)
|
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
|
| |
| | |
Approximating data that might be linear:
Worked example
TI-83/84 worked example
I have more extensive web pages on linear regression and correlation coefficients for my Math 160
section. They are in Topic 8 at Topics in Statistics.
I will create TI-84C versions of those pages as time permits.
|
|
| |

