Please note that the calculator used to produce the graphs on this page had just been used
to produce the graphs and screen images from the web page 238601.htm.
As a result there is some residual material on this calculator.
Figure 1
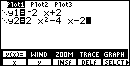
|
Figure 1 is taken from the y(x)= screen on a TI-86 after we have defined
the two functions. The first function is a straight line, and the second is a quadratic which will
be graphed as a parabola. |
Figure 2
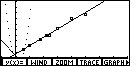
| Pressing   moves the display to Figure 2. Here we see some unexpected items.
For one thing, the graph shows a number of points that are not related to this problem at all.
Second, there are two straight lines that have been graphed here,
only one of which has slope equal to – 2.
Third, the graph of the parabola is made up of separated points.
And, fourth, the WINDOW settings for the graph are not obvious.
moves the display to Figure 2. Here we see some unexpected items.
For one thing, the graph shows a number of points that are not related to this problem at all.
Second, there are two straight lines that have been graphed here,
only one of which has slope equal to – 2.
Third, the graph of the parabola is made up of separated points.
And, fourth, the WINDOW settings for the graph are not obvious. |
Figure 3
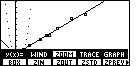
| We will use the ZOOM feature to change the WINDOW settings to the standard values.
To do this we press  to open the sub-menu shown in Figure 3.
Then, to select ZSTD we press to open the sub-menu shown in Figure 3.
Then, to select ZSTD we press  . This will produce Figure 4. . This will produce Figure 4. |
Figure 4
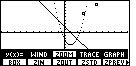
| In Figure 4 we have the more usual Window settings, namely both x and
y range between – 10 and 10. In addition, the second straight line from Figures 2 and 3,
the line that approximated the plotted points, has disappeared.
That line was the drawing of the regression equation computed from those points.
It was left over from earlier work on this calculator. On the TI-86 we can obtain that regresssion
equation, after performing the LinR analysis, by asking the calculator to
DRREG, DRaw the REGression equation. However, that drawing disappears as soon as
we have the calculator recreate a graph. Changing the WINDOW settings via the ZSTD
option forces the TI-86 to reconstruct the graph.
We still have the points plotted, although we can only see two of them within the given range,
and the parabola is made up of disconnected dots. |
Figure 5
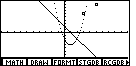
| To make the parabola appear as connected points, we will close the submenu,
via the  key, and then use the key, and then use the
 key to shift the main menu display
to the next set of options, shown in Figure 5.
From that set of options we select FORMT by pressing the key to shift the main menu display
to the next set of options, shown in Figure 5.
From that set of options we select FORMT by pressing the
 key.
This will open the options screen shown in Figure 6. key.
This will open the options screen shown in Figure 6.
|
Figure 6

| The DrawDot option needs to be changed. We
use the  to move the highlight
down to the DrawLine option and then press to move the highlight
down to the DrawLine option and then press
 to selct that option. The result
is shown in Figure 7. to selct that option. The result
is shown in Figure 7. |
Figure 7

| Now that the option is set as we want it, we press
 to redraw the graph. to redraw the graph. |
Figure 8
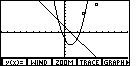
| Here the parabola is connected, but we still have those
plotted points left over from some earlier work. To clear those points we need to turn off the
statistical plot. To do that we need to return to
the STAT menu. |
Figure 9
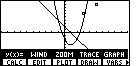
| We press   to open the STAT menu shown in Figure 9. From that menu we press
to open the STAT menu shown in Figure 9. From that menu we press
 to choose PLOT.
That will open the window in Figure 10. to choose PLOT.
That will open the window in Figure 10. |
Figure 10
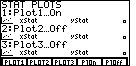
| Now we can see that Plot1 is indeed On. The
easiest remedy will be to turn off
all of the plots. We do this by using the  key to
select PlOff. That option causes the PlOff command to be pasted onto the
base window in Figure 11. key to
select PlOff. That option causes the PlOff command to be pasted onto the
base window in Figure 11. |
Figure 11

| Once the command has been pasted onto the window, we press
 to perform it. The
calcualtor responds with Done. to perform it. The
calcualtor responds with Done.
Then, we return to the graph by pressing  . .
|
Figure 12
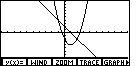
| In Figure 12 we finally see the graph without the distracting
plotted points. Our purpose here is to use the ISECT
command to find the two points of intersection.
We could modify the WINDOW settings to have the graph come close
to the one presented in the text, but that will not
be necessary. |
Figure 13
| To get to the ISECT option we need to use
the  key to make the MATH
option appear in the main menu, and then use key to make the MATH
option appear in the main menu, and then use  to open the MATH sub-menu.
The result is shown in Figure 13.
ISECT is still a step away.
We will need to press
to open the MATH sub-menu.
The result is shown in Figure 13.
ISECT is still a step away.
We will need to press  to see
more options in the MATH sub-menu. to see
more options in the MATH sub-menu. |
Figure 14
| We find ISECT as the third item in the
sub-menu.
Press  to select that option. to select that option. |
Figure 15
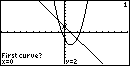
| ISECT goes through a number of steps. First, we need to choose the two curves to
use. It is possible that we would have more than 2 curves graphed at the same time.
The calculator wants us to choose the two graphs to use. This seems a bit superfluous
here given that there are only two functions on this graph. However, we will
have to play along with the calcualtor.
The TI-86 is proposing the first function as one of the two curves.
We press  to accept that choice. to accept that choice.
|
Figure 16
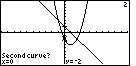
| In Figure 16 the TI-86 proposes the second function as the the second curve.
Again, press  to accept that choice. to accept that choice. |
Figure 17
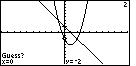
| Now the calculator is asking for a Guess, and it is proposing
the point (0,– 2) as such a guess.
We want to be sure that the calculator finds the left point of intersection. Therefore,
we will improve the guess to help the calculator. We do this
by pressing the  key to move the
Guess closer to the point of intersection. key to move the
Guess closer to the point of intersection. |
Figure 18
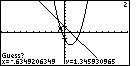
| In Figure 18 we have a Guess that is reasonably close to the
left point of intersection.
We press  to accept that point and have the calculator do the rest of the work. to accept that point and have the calculator do the rest of the work. |
Figure 19
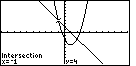
| The TI-86 has determined that the left point of
intersection is (– 1,4).
Now we want to obtain the coordinates of the other point of intersection.
To do this we step through the same sequence of screens, but changing our Guess
so that it is close to the right point of intersection.
|
Figure 20
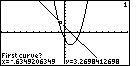
| We press  to leave Figure 19. This will
return us to the main graph menu.
There choose the MATH option, use the MORE key to display new options in the sub-menu, and
select ISECT. The calculator proposes the first curve as one of the two curves to use.
We use the to leave Figure 19. This will
return us to the main graph menu.
There choose the MATH option, use the MORE key to display new options in the sub-menu, and
select ISECT. The calculator proposes the first curve as one of the two curves to use.
We use the  key to accept that choice. key to accept that choice. |
Figure 21
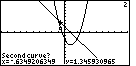
| The calculator proposes the second curve as the other curve to use.
We use the  key to accept that choice. key to accept that choice. |
Figure 22
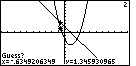
| The TI-86 proposes a point to use as the Guess. We do not
want to use that guess because it is too close to the left point
of intersection.
Therefore, we will use the  to shift the
guess close to the right point of intersection. to shift the
guess close to the right point of intersection. |
Figure 23
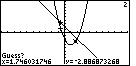
| In Figure 23 the new Guess point has been set. Press  to accept that value.
to accept that value. |
Figure 24
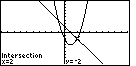
| ISECT has done its work. The right point of intersection
is identified as (2,– 2).
|



 moves the display to Figure 2. Here we see some unexpected items.
For one thing, the graph shows a number of points that are not related to this problem at all.
Second, there are two straight lines that have been graphed here,
only one of which has slope equal to – 2.
Third, the graph of the parabola is made up of separated points.
And, fourth, the WINDOW settings for the graph are not obvious.
moves the display to Figure 2. Here we see some unexpected items.
For one thing, the graph shows a number of points that are not related to this problem at all.
Second, there are two straight lines that have been graphed here,
only one of which has slope equal to – 2.
Third, the graph of the parabola is made up of separated points.
And, fourth, the WINDOW settings for the graph are not obvious. 
 to open the sub-menu shown in Figure 3.
Then, to select ZSTD we press
to open the sub-menu shown in Figure 3.
Then, to select ZSTD we press  . This will produce Figure 4.
. This will produce Figure 4.

 key, and then use the
key, and then use the
 key to shift the main menu display
to the next set of options, shown in Figure 5.
From that set of options we select FORMT by pressing the
key to shift the main menu display
to the next set of options, shown in Figure 5.
From that set of options we select FORMT by pressing the
 key.
This will open the options screen shown in Figure 6.
key.
This will open the options screen shown in Figure 6.

 to move the highlight
down to the DrawLine option and then press
to move the highlight
down to the DrawLine option and then press
 to selct that option. The result
is shown in Figure 7.
to selct that option. The result
is shown in Figure 7. 
 to redraw the graph.
to redraw the graph. 


 to open the STAT menu shown in Figure 9. From that menu we press
to open the STAT menu shown in Figure 9. From that menu we press
 to choose PLOT.
That will open the window in Figure 10.
to choose PLOT.
That will open the window in Figure 10.
 key to
select PlOff. That option causes the PlOff command to be pasted onto the
base window in Figure 11.
key to
select PlOff. That option causes the PlOff command to be pasted onto the
base window in Figure 11.
 to perform it. The
calcualtor responds with Done.
to perform it. The
calcualtor responds with Done. .
.


 key to make the MATH
option appear in the main menu, and then use
key to make the MATH
option appear in the main menu, and then use  to open the MATH sub-menu.
The result is shown in Figure 13.
ISECT is still a step away.
We will need to press
to open the MATH sub-menu.
The result is shown in Figure 13.
ISECT is still a step away.
We will need to press  to see
more options in the MATH sub-menu.
to see
more options in the MATH sub-menu.
 to select that option.
to select that option. 
 to accept that choice.
to accept that choice.

 to accept that choice.
to accept that choice. 
 key to move the
Guess closer to the point of intersection.
key to move the
Guess closer to the point of intersection. 
 to accept that point and have the calculator do the rest of the work.
to accept that point and have the calculator do the rest of the work. 

 to leave Figure 19. This will
return us to the main graph menu.
There choose the MATH option, use the MORE key to display new options in the sub-menu, and
select ISECT. The calculator proposes the first curve as one of the two curves to use.
We use the
to leave Figure 19. This will
return us to the main graph menu.
There choose the MATH option, use the MORE key to display new options in the sub-menu, and
select ISECT. The calculator proposes the first curve as one of the two curves to use.
We use the  key to accept that choice.
key to accept that choice.
 key to accept that choice.
key to accept that choice. 
 to shift the
guess close to the right point of intersection.
to shift the
guess close to the right point of intersection.
 to accept that value.
to accept that value. 