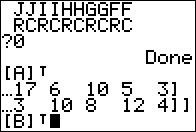Figure 01
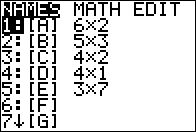
|
To find the transpose of [A] we
will need to donstruct the command
[A]T. To do this we open the
matrix menu as shown in Figure 01.
Then, because the desired matrix is already highlighted we can press
 to paste that name onto the home window. to paste that name onto the home window.
|
Figure 02
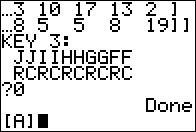
|
Figure 02 shows that we have the name of the desired matrix
on the home window.
|
Figure 03
|
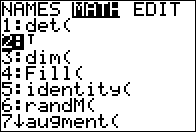
We return to the matrix menu, use  to move tot he MATH option and then use
to move tot he MATH option and then use
 to highlight the T
item as shown in Figure 03. Then press to highlight the T
item as shown in Figure 03. Then press  to paste that onto our command.
to paste that onto our command.
|
Figure 04
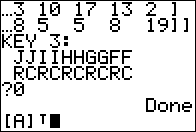
|
Now that the command is correctly formed, as in Figure 04,
we press  to have the calculator perform the command. to have the calculator perform the command.
|
Figure 05
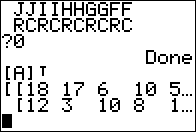
|
The result, or at least the first four and a bit of the fifth column, is shown in Figure 05.
|
Figure 06
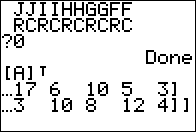
|
We can use the  key to slide the display over
so that we can see the rest of the matrix, as shown in Figure 06.
We note that the transposed matrix is exactly as we had expected
from the discussion above. key to slide the display over
so that we can see the rest of the matrix, as shown in Figure 06.
We note that the transposed matrix is exactly as we had expected
from the discussion above.
|
Figure 07
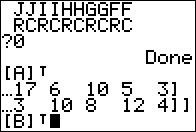
|
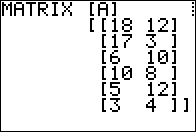
Recall that [B] is a 5 x 3
matrix so we expect that
[B]T will be a
3 x 5 matrix. Figure 07 shows the
command needed to find the transpose of [B].
|
Figure 08
|
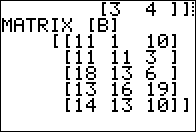
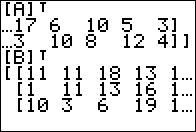
Figure 08 shows the result of that transpose,
although again we can only see part of the answer.
|
Figure 09
|
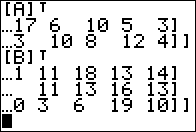
The rest of the resulting matrix is shown in Figure 09.
|
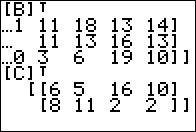
Figure 10
|
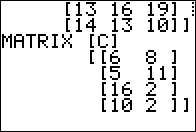
For Figure 10 we form and execute the command to find the
transpose of [C].
|
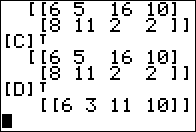
Figure 11
|
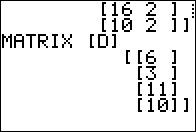
For Figure 11 we form and execute the command to find the
transpose of [D].
|
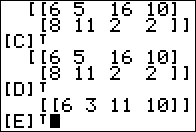
Figure 12
|
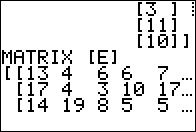
For Figure 12 we simply add the command to find [E] transpose.
.
|
Figure 13

|
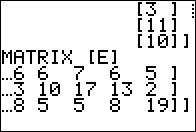
Figure 13 shows the result, again a value that showl be compared to the value
of the original matrix [E].
|
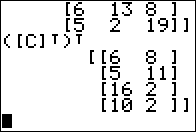
Figure 14
|
Finally, in Figure 14, we see a demostration of the fairly obvious fact that the
transpose of the transpose of a matrix is just the original matrix.
|
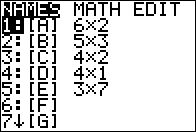
 to paste that name onto the home window.
to paste that name onto the home window.
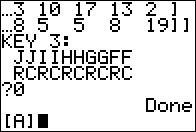

 to move tot he MATH option and then use
to move tot he MATH option and then use
 to highlight the T
item as shown in Figure 03. Then press
to highlight the T
item as shown in Figure 03. Then press  to paste that onto our command.
to paste that onto our command.
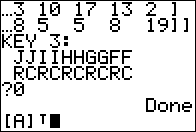
 to have the calculator perform the command.
to have the calculator perform the command.
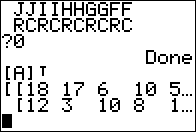
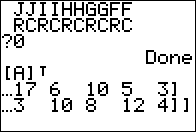
 key to slide the display over
so that we can see the rest of the matrix, as shown in Figure 06.
We note that the transposed matrix is exactly as we had expected
from the discussion above.
key to slide the display over
so that we can see the rest of the matrix, as shown in Figure 06.
We note that the transposed matrix is exactly as we had expected
from the discussion above.