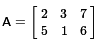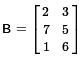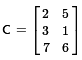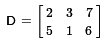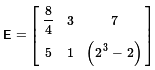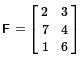Matrix: Equality
Return to Roadmap 3
In order for two matrices to be equal they must be identical.
That is they have the same dimensions and the same values in each position.
Thus if we define six matrices
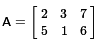
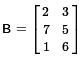
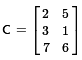
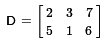
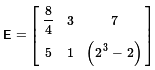
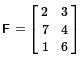
then certainly A = D.
It is also true that A = E because they have the same dimensions
and the "values"
of the items in the
two matrices match even though the values in E
may need to be simplified.
And, of course, then D = E.
Those are the only equalities among the six matrices.
B and F are almost identical, but the elements in row 2 column 2
are different: it is 5 in B and 4 in F.
e two matrices A and B have the same values but they have different dimensions.
Therefore they are not equal.
B and C have the same dimensions, and they have the same six values, but the values do
not appear in the same positions. Therefore they are not equal.
Return to Roadmap 3
©Roger M. Palay Saline, MI 48176 February, 2017