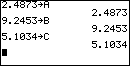


 . If we start a line with
the "store" command then the calculator automatically supplies the Ans variable.
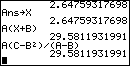
And, we conclude Figure 2 by finding the value of A(X+B),
namely, 29.5811931991.
. If we start a line with
the "store" command then the calculator automatically supplies the Ans variable.
And, we conclude Figure 2 by finding the value of A(X+B),
namely, 29.5811931991.
| Note that the TI-86 and the TI-85 have slightly different keys. This page uses the keys associated with the TI-86. The differences are in the "2nd" functions on some of the keys used here. The TI-85 keys will have the same key-face symbol unless otherwise noted. |
Example 3 in the textbook gives the problem:
| If x = | c – ab a – b |
find the value of the expression a(x+b) |
| a ( c – b2 ) a – b |
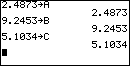
| We start by assigning some arbitrary values to A, B, and C. We use "wierd" values so that we are less likely to produce accidentally identical answers even if we had an error. Using values such as 1, 0, and 2 would not give a good test of our work. In any case, the calculator is going to do the arithmetic! We do not care if it has to work a little harder to use wierd values. |

| In Figure 2 we find the value of the expression
  . If we start a line with
the "store" command then the calculator automatically supplies the Ans variable.
And, we conclude Figure 2 by finding the value of A(X+B),
namely, 29.5811931991. . If we start a line with
the "store" command then the calculator automatically supplies the Ans variable.
And, we conclude Figure 2 by finding the value of A(X+B),
namely, 29.5811931991.
|

| The answer
should be |
This process of testing an algebraic simplification by evalating the original problem and the final answer with arbitrary (and "wierd") values is an important and useful application of the calculator.
PRECALCULUS: College Algebra and Trigonometry
© 2000 Dennis Bila, James Egan, Roger Palay